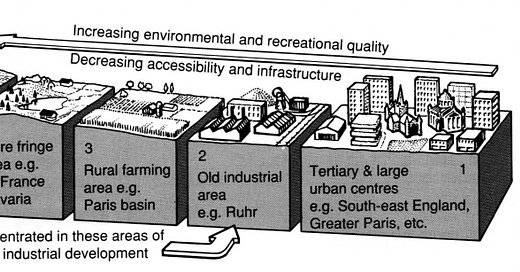
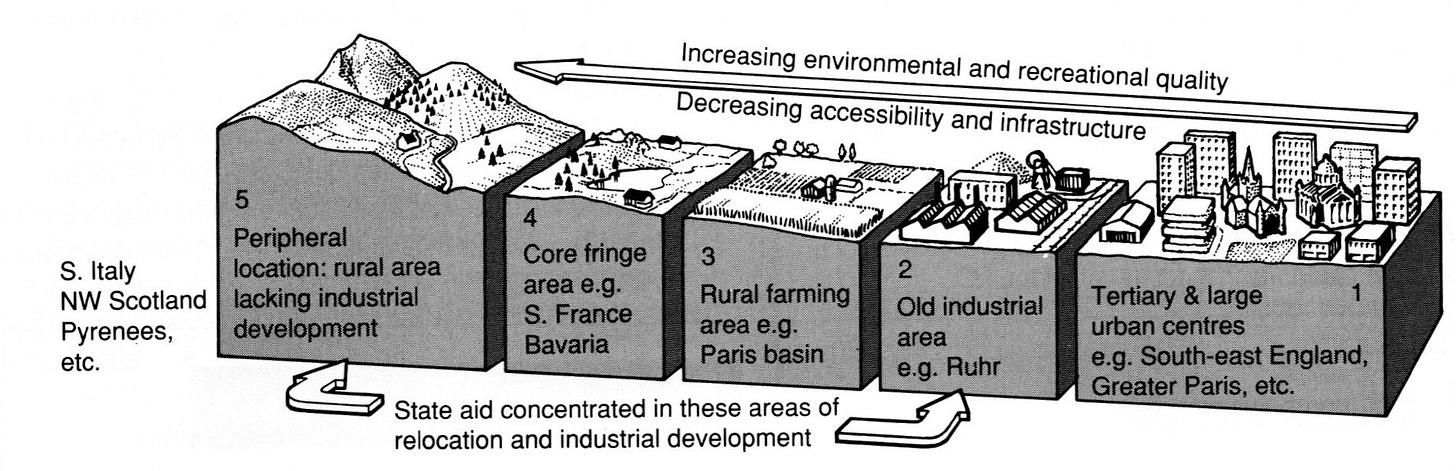
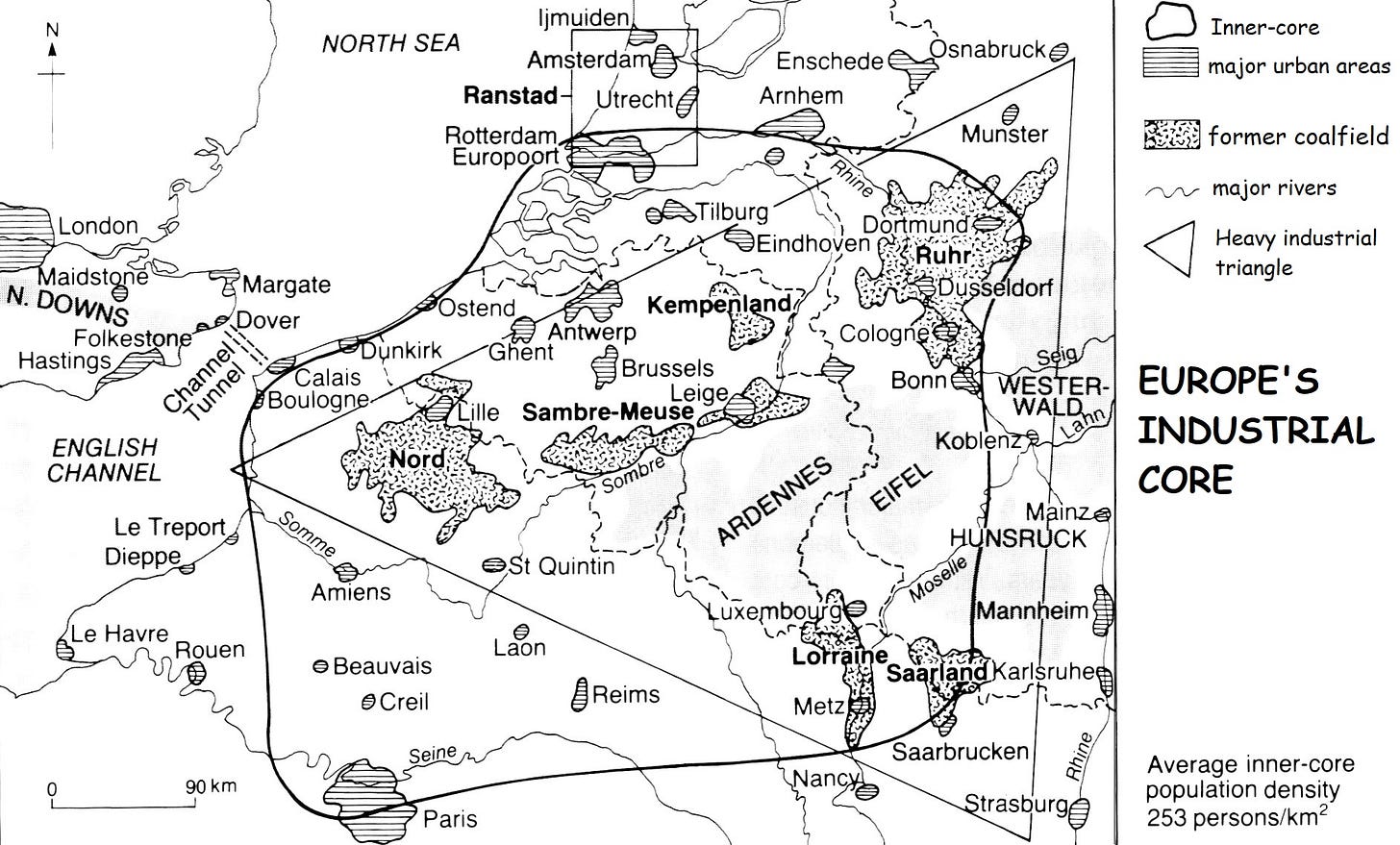
The uneven distribution of industrial activity across Europe, characterised by the concentration of industries in densely populated areas and the underdevelopment of peripheral, rural regions, is a complex phenomenon rooted in both physical and economic factors.
Significant disparities between densely populated urban areas and peripheral rural regions characterise Europe's industrial landscape.
Industrial Overconcentration in Densely Populated Areas
Physical Factors
Densely populated areas in Europe often benefit from:
Resource Availability: Historically, the concentration of industries in certain regions was driven by the availability of natural resources. Coalfields in the Ruhr Valley, Germany, and iron ore deposits in Lorraine, France, attracted industries such as steelmaking and manufacturing.
Accessibility: Densely populated areas often have better transportation infrastructure networks, including railways, roads, and ports, making them more accessible to markets, trade routes and suppliers. This advantage facilitates the flow of goods and services, attracting industries.
Climate: Certain industries, such as textiles and agriculture, are sensitive to climatic conditions. Regions with favourable climates, such as the Mediterranean, have historically attracted industries related to these sectors.
Favourable topography, with flat or gently rolling terrain that facilitates infrastructure development
Economic Factors
Several economic forces drive industrial concentration in urban areas:
Agglomeration Economies: The clustering of industries in specific locations can create economies of scale and scope. By sharing infrastructure, labour pools, and knowledge, firms can reduce costs and increase efficiency. This has led to the concentration of industries in major cities and industrial hubs. Larger consumer markets, allow for economies of scale
Historical Legacy: The industrialisation process in Europe began in certain regions, often due to historical factors such as political stability, technological advancements, and entrepreneurial activity. This early development created a concentration of industries that has persisted over time.
Government Policies: Government policies, such as investment incentives, infrastructure development, and industrial zoning, can influence the location of industries. In some cases, governments have actively promoted the concentration of industries in specific regions.
Better infrastructure, including transportation networks, utilities, and telecommunications
Access to financial services and investment capital
Presence of universities and research institutions, fostering innovation and skilled labour
Industrial Underdevelopment in Peripheral, Rural Regions
Physical Challenges
Peripheral rural regions often face:
Geographic isolation, with greater distances from major markets and transportation hubs
Challenging terrain, such as mountainous areas or remote islands, increasing transportation costs
Limited natural resources or difficulty in accessing them
Economic Obstacles
Rural areas struggle with several economic disadvantages:
Smaller local markets, making it difficult to achieve economies of scale
Limited access to skilled labour, as younger, educated workers often migrate to urban areas
Underdeveloped infrastructure, including transportation networks and high-speed internet
Reduced access to financial services and investment capital
Fewer opportunities for knowledge spillovers and innovation networks
Consequences and Trends
The disparity between urban and rural areas has led to significant challenges:
Rural depopulation, with many regions experiencing population decline
Aging populations in rural areas, as younger people move to cities for better opportunities
Economic stagnation in peripheral regions, widening the urban-rural divide
Increased pressure on urban infrastructure due to overconcentration
Policy Responses
European policymakers are addressing these challenges through various initiatives:
The EU's rural development policy, which aims to strengthen rural economies and improve quality of life
Investments in rural infrastructure, including broadband internet and transportation networks
Support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in rural areas
Promotion of smart specialisation strategies to leverage regional strengths
Encouragement of remote work and digital technologies to bridge the urban-rural divide
Examples of Industrial Overconcentration and Underdevelopment
The Ruhr Valley, Germany: A prime example of industrial overconcentration, the Ruhr Valley has a long history of heavy industry, including coal mining, steelmaking, and manufacturing. However, the decline of these industries in recent decades has led to economic challenges and deindustrialisation.
The Mezzogiorno, Italy: The southern regions of Italy, known as the Mezzogiorno, have historically experienced underdevelopment compared to the more industrialised north. This is due to a combination of factors, including geographical isolation, limited infrastructure, and a lack of investment.
In conclusion, the uneven distribution of industrial activity in Europe is a complex phenomenon influenced by a variety of physical and economic factors. While the concentration of industries in densely populated areas has historically provided economic benefits, it has also led to challenges such as environmental pollution, congestion, and social inequality. Addressing the underdevelopment of peripheral, rural regions requires a multifaceted approach that takes into account the specific needs and challenges of these areas.
While progress has been made, addressing the imbalance between densely populated areas and peripheral regions remains an ongoing challenge for European policymakers and regional planners.
References
ESPON Policy Brief on Shrinking Rural Regions.pdf
New reports highlight CAP's role in strengthening rural areas - European Commission (europa.eu)
EU rural development policy (europa.eu)
How does population distribution affect infrastructure development? | TutorChase
Industrialization as an Historical Process — EGO (ieg-ego.eu)
FEEL FREE TO BUY ME A COFFEE IF YOU LIKE MY FREE RESOURCES
or one of my inexpensive books at
Amazon.co.uk: Ritchie Cunningham: books, biography, latest update